Peripheral Angiography (PAG)
Peripheral Angiography (PAG) | Cardiology | Apex Hospitals
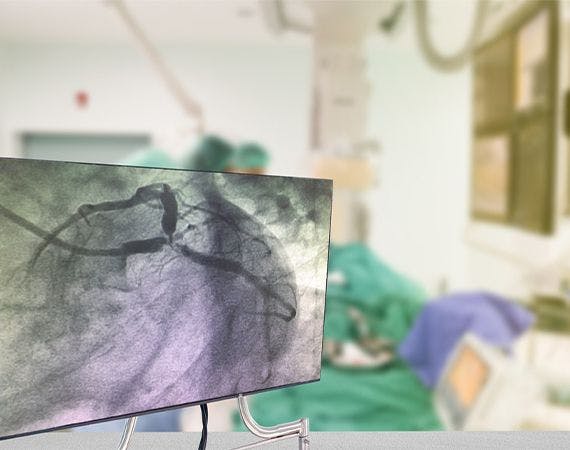
What is peripheral angiography?
Peripheral angiography is a medical imaging procedure used to visualize and evaluate the blood vessels outside the heart and brain, specifically those in the body's peripheral regions. It is commonly performed to assess the blood flow in the arteries and veins of the legs, arms, pelvis, and other peripheral areas.
The procedure involves injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels, which makes them visible on X-ray images. These images help healthcare professionals identify abnormalities or blockages in the blood vessels that may affect blood flow. Peripheral angiography is often used to diagnose conditions such as peripheral artery disease (PAD), aneurysms, and vascular malformations.
Procedure Details
Before:
You will receive detailed instructions regarding dietary restrictions 24 hours before the peripheral angiogram. You will be advised to abstain from eating or drinking for 6 to 8 hours before the procedure. You must inform your doctor about all your medications, including over-the-counter drugs, herbs, and vitamins. Your doctor may instruct you to temporarily refrain from taking certain medications, but it's essential not to discontinue any medication without your doctor's approval.
In addition, communicate any allergies you may have, particularly to substances such as iodine, latex, rubber products, penicillin, or X-ray dye. If you are pregnant or have a history of bleeding problems, inform your doctor or nurse beforehand. For your comfort and safety during the procedure, leaving all jewellery at home is advisable. Lastly, arrange for someone to drive you home after the peripheral angiogram.
During:
A highly trained doctor, accompanied by a team of nurses and technicians, conducts the peripheral angiogram, typically in a hospital or outpatient clinic setting.
Before the procedure, a nurse will establish an IV (intravenous line) in your arm to administer the necessary medications and fluids. It's important to note that you will be awake throughout the test. Subsequently, the nurse will clean and prepare the area where the doctor works, commonly the artery in your groin. To minimise discomfort, a local anaesthetic will be applied to numb the needle puncture site.
The doctor will then perform a needle puncture through your skin and into the artery, introducing a slender, elongated tube known as a catheter into the artery. While you may experience some pressure, any pain should be minimal. To enhance visibility on X-rays, the doctor will inject a small quantity of contrast dye through the catheter. This dye may induce a brief sensation of warmth or flushing, lasting only a few seconds.
After:
Following the procedure, you'll be directed to a recovery room briefly. To mitigate the risk of bleeding, the nurse will apply pressure to the puncture site for approximately 10 to 20 minutes, followed by applying a bandage to the wound. During this time, it's advised not to move the leg involved in the catheter insertion while the nurse diligently monitors for any signs of bleeding or swelling.
Before your departure, you will receive detailed written instructions on home care to ensure a smooth recovery process.
Speak to our expert about Peripheral Angiography
Connect with our expert to gain valuable insights and information about Peripheral Angiography. Our knowledgeable team is ready to address your queries and provide guidance and support. Your vascular health is our priority, and we are here to ensure you clearly understand Peripheral Angiography. Schedule a consultation with our expert today for personalized assistance.
FAQS
Health In A Snap, Just One App.
KNOW MORE
